
The Bow-Fingered Gecko is a fascinating reptile with a unique distribution around the world. These geckos can be found in various regions of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, Thailand, the Malay Peninsula, and Papua New Guinea. Within Indonesia, they are present on islands such as Java, Sulawesi, Halmahera, Flores, Komodo, Lombok, Pulau Kalao, and Sumbawa.
Key Takeaways:
- The Bow-Fingered Gecko is found across several Southeast Asian countries.
- Within Indonesia, there are specific species of Bow-Fingered Geckos that are endemic to certain islands.
- These geckos have unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in their respective environments.
- Conservation efforts are crucial to protect the habitats of these geckos and ensure their survival.
- Further research is needed to enhance our understanding of the behavior and distribution of Bow-Fingered Geckos.
Exploring the Geckos of Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is home to an array of gecko species, including the captivating Bow-Fingered Gecko. These fascinating reptiles can be found in various countries within the region, each with its own unique gecko habitats and distribution patterns.
One of the key countries where the Bow-Fingered Gecko resides is Indonesia. With its diverse landscape and numerous islands, Indonesia is a hotspot for gecko diversity. The gecko species can be found on islands like Java, Sulawesi, Halmahera, Flores, Komodo, Lombok, Pulau Kalao, and Sumbawa. Each of these islands offers a different environment and ecosystem, allowing for specific adaptations and behaviors among the geckos.
In addition to Indonesia, other countries in Southeast Asia also boast a population of Bow-Fingered Geckos. Thailand, with its rich biodiversity, is another prime location for these geckos. The Malay Peninsula, which spans across Malaysia and southern Thailand, is teeming with gecko species, including the Bow-Fingered Gecko. These geckos can be found in various regions within Thailand, highlighting the importance of preserving their natural habitats.
Papua New Guinea, located in the southwestern Pacific region, is yet another country where the Bow-Fingered Gecko thrives. The country is known for its vast rainforests and diverse wildlife, making it an ideal habitat for these geckos. It is crucial to protect the natural environment of Papua New Guinea to ensure the survival of this vibrant gecko population.
Gecko Distribution in Southeast Asia
To summarize, the Bow-Fingered Gecko has a widespread distribution in Southeast Asia, specifically in countries like Indonesia, Thailand, the Malay Peninsula, and Papua New Guinea. Within Indonesia, there are specific gecko species that are endemic to certain islands, adding to the region’s biodiversity. These geckos have adapted to their respective habitats, exhibiting unique characteristics and behaviors. As we explore the geckos of Southeast Asia, it is essential to recognize the importance of preserving their habitats and supporting conservation efforts to ensure the survival of these captivating creatures.
| Country | Major Islands |
|---|---|
| Indonesia | Java, Sulawesi, Halmahera, Flores, Komodo, Lombok, Pulau Kalao, Sumbawa |
| Thailand | Various regions within the country |
| Malay Peninsula | Various regions within Malaysia and southern Thailand |
| Papua New Guinea | Throughout the country |
“The Bow-Fingered Gecko has established its presence in various parts of Southeast Asia, showcasing its remarkable adaptability and resilience. As we continue to explore the geckos of this region, let us remember the importance of protecting their habitats and ensuring the longevity of these captivating creatures.”
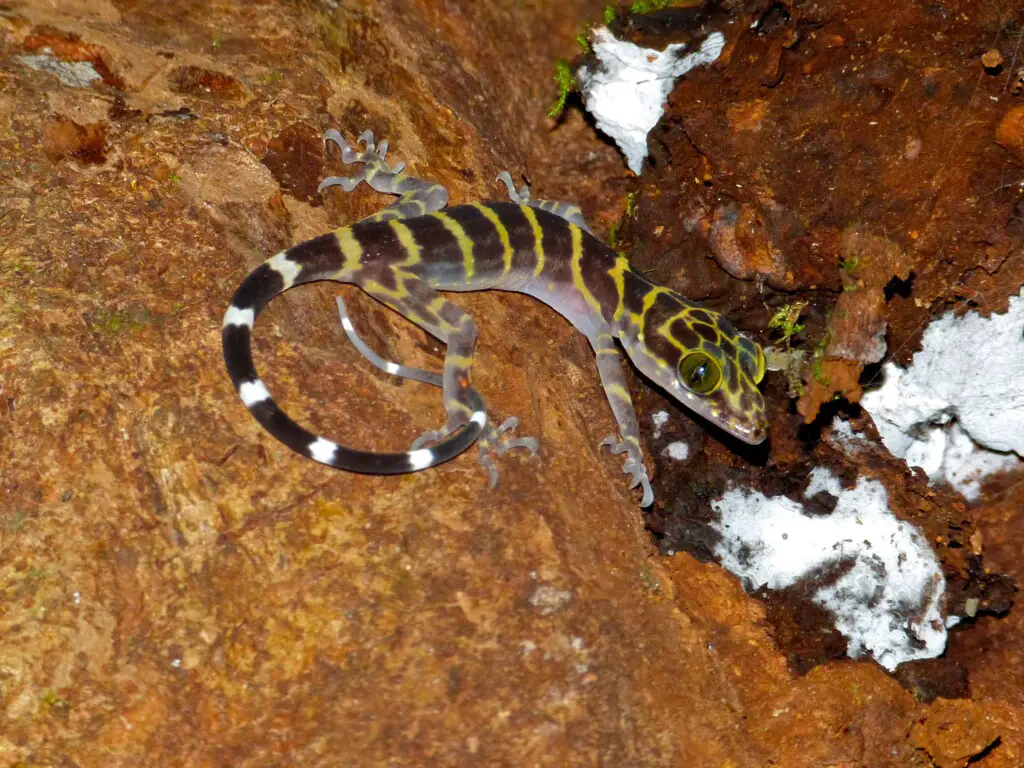

Indonesia boasts a rich diversity of gecko species, and the Bow-Fingered Gecko is no exception. These geckos have adapted to their specific island habitats, showcasing remarkable traits and behaviors.
The Bow-Fingered Gecko, scientifically known as Gehyra mutilata, is characterized by its distinctive finger-like extensions on its toes. These remarkable structures help them navigate their environment, climbing surfaces with ease. With their slender bodies and reddish-brown coloration, they blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them excellent hunters.
One interesting aspect of the Bow-Fingered Gecko in Indonesia is its dominance in specific island ecosystems. These geckos have evolved to occupy niche habitats, such as the rocky terrain on Komodo Island or the lush forests of Pulau Kalao. Their specialized adaptations enable them to thrive in these unique environments, contributing to the overall biodiversity of Indonesia.
Indonesia’s islands are home to a myriad of gecko species, and several of them are specific to certain islands. For example, the Flores Island Bow-Fingered Gecko (Gehyra vorax) is endemic to Flores, showcasing distinct characteristics that set it apart from its mainland counterparts. Similarly, the Sumbawa Island Bow-Fingered Gecko (Gehyra reticulata) can only be found on Sumbawa Island. These island-specific species highlight the remarkable adaptations and evolutionary processes that have shaped Indonesia’s gecko diversity.
| Island | Endemic Gecko Species |
|---|---|
| Flores | Gehyra vorax |
| Sumbawa | Gehyra reticulata |
“The Bow-Fingered Gecko’s distribution in Indonesia showcases the incredible diversity of gecko species found in the country’s various islands. Each species possesses unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in their respective island habitats, contributing to the overall richness of Indonesia’s wildlife.”
Conservation efforts play a vital role in protecting the Bow-Fingered Gecko and its surrounding ecosystems. As these geckos face habitat loss and potential threats from human activities, it is crucial to raise awareness and implement measures to preserve their natural habitats. By doing so, we can ensure the continued existence of these fascinating gecko species and uphold Indonesia’s remarkable biodiversity.
The Thriving Gecko Population in Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea is a treasure trove for gecko enthusiasts, with the Bow-Fingered Gecko being a prominent inhabitant. This beautiful country, situated in the western Pacific, is home to a diverse range of gecko species, and the Bow-Fingered Gecko is one of the most abundant. Its population thrives in the lush rainforests and coastal regions of Papua New Guinea, where it has found the perfect combination of habitat and resources to thrive.
The gecko habitats in Papua New Guinea are as varied as the species themselves. From dense jungles to rocky cliffs and mangrove swamps, these geckos have adapted to a wide range of environments. They are skilled climbers, using their unique bow-shaped fingers to grip onto various surfaces, allowing them to explore their surroundings with ease.
The gecko distribution map in Papua New Guinea reveals the widespread presence of the Bow-Fingered Gecko throughout the country. This population distribution highlights the significance of Papua New Guinea as a hotspot for gecko diversity and showcases the adaptation capabilities of these fascinating creatures.
| Species | Habitats |
|---|---|
| Bow-Fingered Gecko (Phelsuma cepediana) | Rainforests, coastal regions |
| Golden Bow-Fingered Gecko (Phelsuma laticauda) | Coastal regions, mountainous areas |
| Black-tailed bow-fingered Gecko (Phelsuma nigrocapitata) | Rocky cliffs, mangrove swamps |
“The gecko habitats in Papua New Guinea are as varied as the species themselves.”
Conservation efforts in Papua New Guinea are crucial to ensure the continued thriving population of these geckos. Protection of their natural habitats, such as rainforests and coastal regions, is essential to safeguard their populations and maintain the delicate balance of the ecosystem they inhabit.
- Gecko habitats worldwide
- Diverse range of gecko species
- Significance of Papua New Guinea
- Bow-Fingered Gecko adaptation in varied environments
- Conservation efforts to protect gecko populations
Endemic Geckos of Indonesia’s Islands
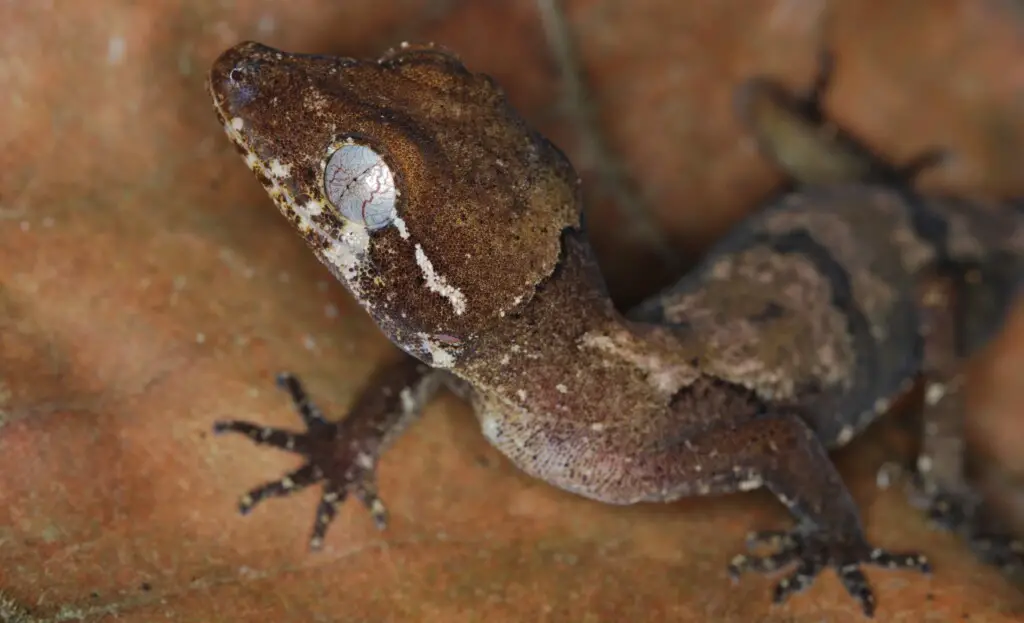
The Indonesian islands are home to a range of endemic gecko species, and the Bow-Fingered Gecko showcases remarkable adaptations on several islands. One such island is Flores, where the Bow-Fingered Gecko, scientifically known as Gehyra gemina, can be found. With its distinctive bow-shaped fingers, this gecko has evolved to thrive in the unique environment of Flores.
Another island with its own endemic species is Komodo, home to the Komodo Bow-Fingered Gecko (Gehyra komodoensis). These geckos have adapted to the rugged terrain and harsh climate of the island, with their strong claws and ability to camouflage among the rocks and vegetation. They are a testament to the incredible biodiversity found on Komodo Island.
The island of Lombok is also home to its own endemic gecko species, the Lombok Bow-Fingered Gecko (Gehyra lombokana). These geckos are known for their vibrant colors and the ability to change their skin patterns to match their surroundings. Their unique adaptations make them well-suited to the diverse habitats found on Lombok.
Pulau Kalao and Sumbawa are two more Indonesian islands that host their own endemic Bow-Fingered Gecko species. The Pulau Kalao Bow-Fingered Gecko (Gehyra kalaoensis) can be found on Pulau Kalao, while the Sumbawa Bow-Fingered Gecko (Gehyra sumbawana) is found on Sumbawa. These geckos have developed specific adaptations to survive and thrive in their respective island habitats.

| Island | Endemic Species |
|---|---|
| Flores | Gehyra gemina |
| Komodo | Gehyra komodoensis |
| Lombok | Gehyra lombokana |
| Pulau Kalao | Gehyra kalaoensis |
| Sumbawa | Gehyra sumbawana |
These endemic gecko species found on the Indonesian islands are a testament to the rich biodiversity and the unique adaptations that have evolved in response to the diverse environments. It is crucial to protect these habitats and the geckos that call them home to ensure the long-term survival of these remarkable species.
Unveiling the Geckos of Thailand
Thailand provides a diverse range of habitats where the Bow-Fingered Gecko thrives in the wild. From lush rainforests to dry savannahs, these geckos have adapted to various environments, making them a fascinating subject of study for researchers and enthusiasts alike.
One of the prominent regions in Thailand where the Bow-Fingered Gecko can be found is the Khao Yai National Park. This protected area is known for its rich biodiversity and is home to numerous reptile species, including our elusive gecko. The park’s dense forests and limestone caves provide ideal conditions for these geckos, offering them ample hiding spots and abundant food sources.
Additionally, the coastal regions of Thailand, such as Phuket and Krabi, are also known to harbor populations of the Bow-Fingered Gecko. The geckos in these areas have adapted to the unique challenges of seaside habitats, including salty air and fluctuating temperatures. Their ability to thrive in such diverse landscapes showcases the remarkable adaptability of these geckos.
Exploring Thailand’s gecko habitats not only provides us with insights into the behavior and distribution patterns of Bow-Fingered Geckos but also highlights the need for their conservation. It is crucial to protect these natural habitats to ensure the survival of this unique gecko species for future generations to appreciate and study.
| Thailand’s Gecko Habitats | Threats to Gecko Habitats |
| Khao Yai National Park | Habitat loss due to deforestation |
| Phuket | Illegal collection for the pet trade |
| Krabi | Climate change |
The Bow-Fingered Gecko’s Range in Malaysia
Malaysia is home to a significant population of Bow-Fingered Geckos, with their range spanning across various states. These geckos are known for their distinctive long fingers, which allow them to cling onto vertical surfaces with ease. Their habitat includes rainforests, limestone caves, and even urban areas, showcasing their adaptability to diverse environments.
One notable state where the Bow-Fingered Gecko is found is Sarawak, located on the island of Borneo. Here, the geckos can be spotted in both rural and urban settings, making use of buildings and trees as their natural perches. Additionally, the state of Perak on the Malay Peninsula is another region where these geckos thrive. The limestone caves and karst landscapes provide suitable conditions for their foraging and breeding activities.
To gain a better understanding of the range and distribution of Bow-Fingered Geckos in Malaysia, researchers have been conducting surveys and studying their behavior. These studies have revealed fascinating insights into their ecological requirements and interactions with their surroundings. By documenting their presence in different states and habitats, conservation efforts can be directed towards preserving their natural habitats and ensuring their long-term survival.
| State | Habitat | Notable Locations |
|---|---|---|
| Sarawak | Rainforests, Urban Areas | Kuching, Miri |
| Perak | Limestone Caves, Karst Landscapes | Gua Tempurung, Gopeng |
As we continue to uncover more about the Bow-Fingered Gecko’s range in Malaysia, it becomes increasingly crucial to protect their habitats and mitigate the threats they face. Habitat destruction, due to urbanization and deforestation, poses a significant risk to these geckos. Conservation organizations and local authorities play a vital role in raising awareness and implementing measures to safeguard these unique reptiles and their ecosystems.
Protecting the Bow-Fingered Gecko’s Habitat
Preserving the habitats of Bow-Fingered Geckos is crucial for their long-term survival and overall ecosystem health. Since each of the countries in which these gecko exists offers diverse ecosystems and habitats that support them, one of the main threats faced by these Geckos is habitat loss due to deforestation and urbanization.
As human activities continue to encroach upon their natural habitats, these geckos are losing essential resources and shelter. Conservation efforts aimed at protecting and restoring their habitats are of utmost importance to ensure the survival of these fascinating gecko species.
Furthermore, illegal pet trade poses a significant risk to the Bow-Fingered Geckos. Due to their unique physical characteristics and fascinating behaviors, these geckos are often targeted by collectors. This illegal trade disrupts their populations and adds further pressure to their already vulnerable status.
To combat these threats, conservation organizations and government agencies are working together to establish protected areas and educate local communities about the importance of preserving the geckos’ habitats. By raising awareness and enforcing legislation against illegal trade, we can safeguard the Bow-Fingered Geckos and the ecosystems they inhabit.
The Importance of Community Engagement
“Preserving the habitats of the Bow-Fingered Geckos is a collaborative effort that requires the engagement of local communities. By involving them in conservation initiatives, we can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards protecting these unique geckos. Community-led conservation programs can lead to sustainable practices that benefit both the geckos and the communities themselves.”
| Threats to Bow-Fingered Geckos | Conservation Measures |
|---|---|
| Habitat loss due to deforestation and urbanization | Establishment of protected areas, reforestation projects, and land-use planning |
| Illegal pet trade | Enforcement of legislation, awareness campaigns, and support for ethical pet trade alternatives |
| Lack of community involvement | Engagement of local communities through education, outreach programs, and sustainable livelihood initiatives |
Studying the Behavior of Bow-Fingered Geckos
Observing the behavior of Bow-Fingered Geckos provides valuable insights into their fascinating lives. These geckos exhibit a range of intriguing behaviors, from their feeding habits to their unique adaptations for survival.
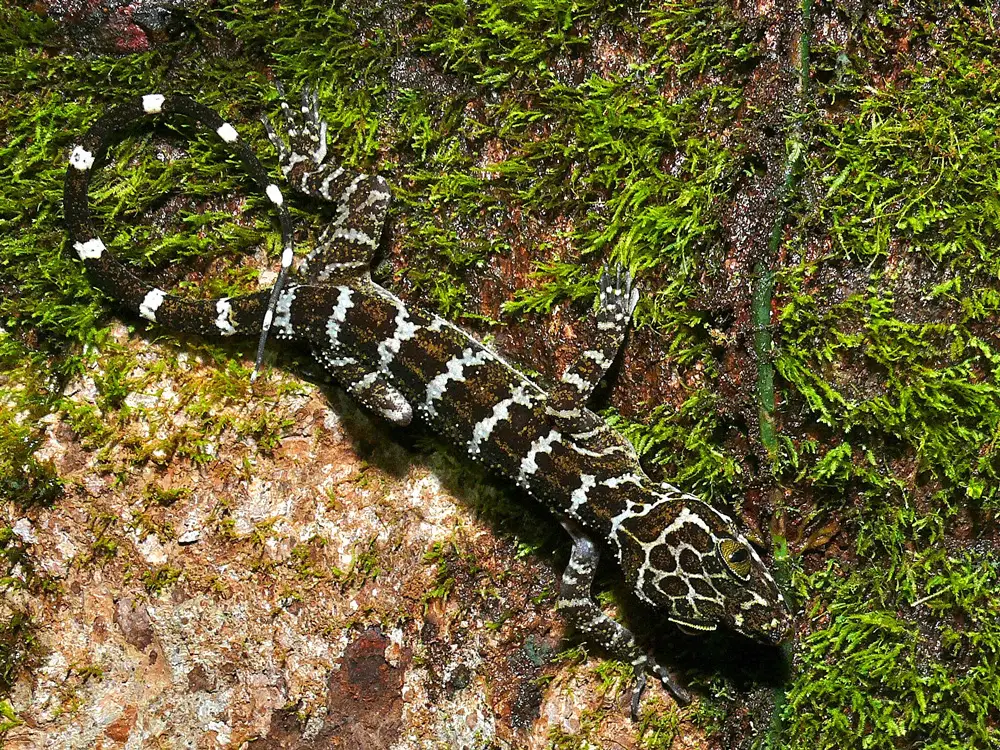

One notable behavior of Bow-Fingered Geckos is their ability to climb vertical surfaces with ease. Their specialized toe pads, equipped with tiny hairs called setae, allow them to adhere to various surfaces, including smooth glass and even upside-down. This remarkable adaptation enables them to navigate their habitats effortlessly and access hidden food sources.
Another interesting behavior exhibited by Bow-Fingered Geckos is their feeding strategy. These geckos are nocturnal hunters and primarily feed on insects and small invertebrates. They employ a sit-and-wait approach, patiently observing their surroundings until prey comes within striking distance. With lightning-fast reflexes, they capture their prey using their tongue, which is equipped with a sticky tip that aids in securing their meal.
Additionally, Bow-Fingered Geckos are known for their unique vocalizations. They communicate through a series of chirps, clicks, and hisses, which vary in frequency and intensity depending on the situation. These vocalizations play a crucial role in mate attraction, territorial defense, and signaling danger to other geckos in the vicinity.
Understanding the Bow-Fingered Gecko’s Behavior through Research
“The behavior of Bow-Fingered Geckos is a fascinating field of study, and ongoing research is shedding light on their complex interactions with their environment and conspecifics,” says Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned herpetologist.
Researchers are employing various methodologies to gain a deeper understanding of the behavior of Bow-Fingered Geckos. These include field observations, laboratory experiments, and advanced technologies such as bioacoustic analysis and genetic studies.
By studying the behavior of Bow-Fingered Geckos, scientists can gain insights into their ecology, reproductive strategies, and responses to environmental changes. This knowledge is crucial for the conservation efforts aimed at preserving their habitats and ensuring the long-term survival of these remarkable geckos.
| Behavior | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Vertical Climbing | Specialized toe pads with setae for adhesion |
| Feeding Strategy | Nocturnal sit-and-wait hunters, sticky-tongue prey capture |
| Vocalizations | Chirps, clicks, and hisses for communication and signaling |
As researchers continue to uncover the intricacies of Bow-Fingered Gecko behavior, our understanding of these unique geckos and their role in Southeast Asian ecosystems expands. The insights gained pave the way for targeted conservation efforts and facilitate the coexistence of these remarkable creatures with human communities.
The Future of Bow-Fingered Gecko Research
As research on Bow-Fingered Geckos progresses, there is much anticipation for exciting findings that will contribute to our knowledge of these remarkable reptiles. Scientists and conservationists are dedicated to studying the behavior, distribution, and conservation needs of these geckos to ensure their long-term survival.
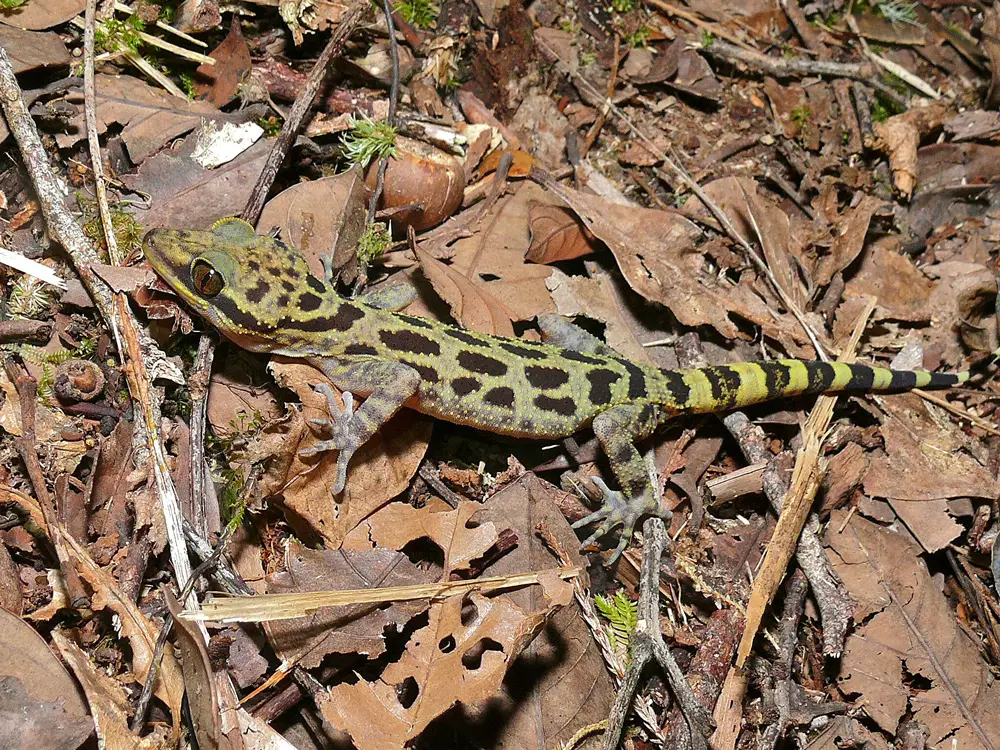

One area of research focuses on understanding the genetic diversity of Bow-Fingered Geckos across their range. By analyzing their DNA, researchers can map out the evolutionary history of these geckos and identify distinct populations. This knowledge is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies and protecting genetic diversity within the species.
Another important aspect of future research is investigating the impact of environmental changes on Bow-Fingered Geckos. With rising temperatures and habitat destruction, it is essential to understand how these geckos adapt and whether they can cope with changing conditions. By studying their physiology and behavior, researchers can identify potential threats and develop targeted conservation plans.
Furthermore, ongoing research is focused on the identification of new species and subspecies of Bow-Fingered Geckos. The Southeast Asian region, particularly Indonesia, is known for its high biodiversity, and there is a possibility of discovering previously unknown gecko species. This discovery would not only contribute to our understanding of gecko evolution but also highlight the importance of protecting their habitats.
In conclusion, the future of Bow-Fingered Gecko research is promising. With advancements in technology and a growing interest in reptile conservation, we can expect to gain valuable insights into the ecology and biology of these geckos. This knowledge will play a crucial role in ensuring the long-term survival of Bow-Fingered Geckos and their habitats.
Conclusion
The Bow-Fingered Gecko’s global distribution highlights the incredible adaptability of these reptiles, while also raising awareness about the need to safeguard their habitats for future generations. This gecko species can be found in Southeast Asia, specifically in countries like Indonesia, Thailand, and Malaysia, as well as Papua New Guinea. Within Indonesia, the geckos are distributed across various islands.
The presence of specific species of Bow-Fingered Geckos endemic to certain Indonesian islands demonstrates the remarkable diversity and specialization within this gecko family. Understanding the gecko’s habitat preferences and distribution patterns is crucial in order to effectively conserve their populations and protect their natural environments.
Conservation efforts are vital in preserving the habitats of the Bow-Fingered Gecko. Threats such as habitat loss and illegal pet trade pose significant challenges to the survival of these geckos. Collaboration between researchers, conservation organizations, and local communities is necessary to implement effective conservation strategies and ensure the long-term survival of these unique reptiles.
As our understanding of the behavior and adaptations of Bow-Fingered Geckos continues to grow, it is important to support ongoing research. The future holds potential for exciting discoveries and advancements in our knowledge of these fascinating geckos. By studying their feeding habits, mating rituals, and unique adaptations, we can gain valuable insights into their ecological role and contribute to their conservation.
FAQ
Where is the Bow-Fingered Gecko found in the World?
The Bow-Fingered Gecko can be found in Southeast Asia, specifically in Indonesia, Thailand, the Malay Peninsula, and Papua New Guinea.
Are there specific species of Bow-Fingered Geckos that are endemic to certain islands in Indonesia?
Yes, there are specific species of Bow-Fingered Geckos that are endemic to certain islands in Indonesia, such as Flores, Komodo, Lombok, Pulau Kalao, and Sumbawa.
What is the significance of understanding the gecko’s habitat and distribution patterns?
Understanding the gecko’s habitat and distribution patterns is important for conservation efforts and for enhancing our knowledge of their behavior, adaptations, and population dynamics.
What are the major threats to the Bow-Fingered Gecko’s habitat?
The major threats to the Bow-Fingered Gecko’s habitat include habitat loss due to deforestation and urbanization, climate change, and illegal pet trade.
How can we protect the habitats of Bow-Fingered Geckos?
Protecting the habitats of Bow-Fingered Geckos requires implementing measures such as habitat conservation, sustainable land use practices, and strict enforcement of laws against illegal wildlife trade.
What are the unique adaptations of Bow-Fingered Geckos?
Bow-Fingered Geckos have unique adaptations such as their ability to climb vertical surfaces using specialized toe pads, their ability to change color to blend in with their surroundings, and their ability to regenerate lost tails.
Are there any ongoing research projects focused on Bow-Fingered Geckos?
Yes, there are ongoing research projects focused on Bow-Fingered Geckos that aim to further understand their behavior, genetics, and ecological roles, as well as the potential medicinal properties of their secretions.
How can I contribute to the conservation of Bow-Fingered Geckos?
You can contribute to the conservation of Bow-Fingered Geckos by supporting organizations involved in their conservation, spreading awareness about the importance of protecting their habitats, and practicing responsible pet ownership.
Are Bow-Fingered Geckos endangered?
The conservation status of Bow-Fingered Geckos varies among species. Some species may be considered endangered or threatened due to habitat loss and other factors, while others may have more stable populations.
Source Links
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Darmandville_bow-fingered_gecko
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marbled_bow-fingered_gecko
- https://www.ecologyasia.com/verts/lizards/yoshi’s-bow-fingered-gecko.htm

